AMD CEO Dr. Lisa Su has confirmed that the next-generation AMD Instinct MI450 data center GPU will utilize TSMC’s advanced 2nm process technology, marking the first time AMD has applied this fabrication node to one of its accelerators. This announcement came during a recent interview with Yahoo Finance, where Su expressed enthusiasm for the upcoming product, stating, “We are very excited about our MI450 generation. It has 2nm technology, the most advanced fabrication capability.” The MI450 is part of AMD’s ongoing push in the AI and data center space, building on a newly announced partnership with OpenAI, which plans to deploy these chips starting next year. The architecture is slated for a full launch in 2026, positioning it as a key contender in high-performance computing.
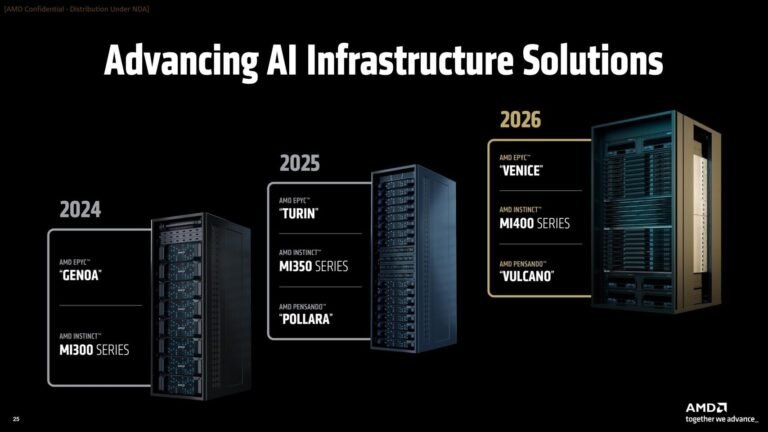
Delving into the technical specifics, the Instinct MI450 incorporates TSMC’s N2P (2nm) process for its core XCD (Accelerator Core Die), while the AID (Active Interposer Die) and MID (Media Interface Die) will use the slightly less advanced N3P (3nm) process, according to insights from leaker Kepler_L2. This hybrid approach reflects the complexities of manufacturing such large and intricate chips. AMD already has hands-on experience with 2nm tech, having taped out wafers for its next-gen EPYC “Venice” processors—powered by Zen 6 architecture—in April 2025, though the MI450’s scale makes it a more ambitious endeavor. An illustrative image from AMD, likely visualizing the MI400 series as a precursor, accompanies the report.
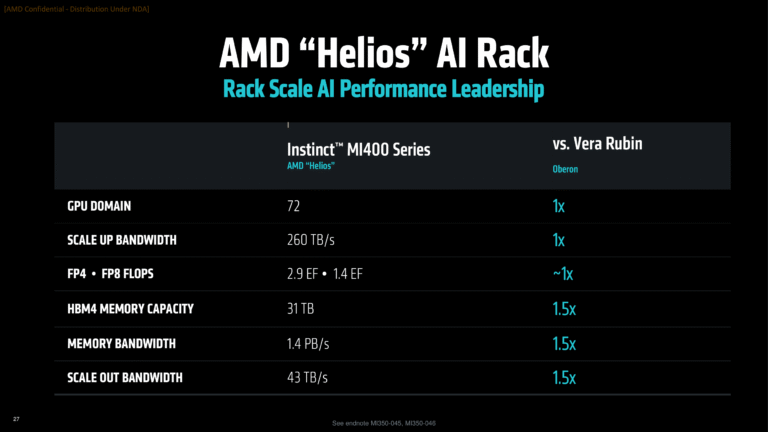
In terms of competitive landscape, the MI450 is designed to rival NVIDIA’s forthcoming Ruby-generation AI accelerators, which rely on TSMC’s 3nm (N3P) process. AMD asserts that the MI450 will match NVIDIA’s Vera Rubin (Oberon) in FP4/FP8 compute speeds but surpass it with 1.5 times the memory capacity and bandwidth, as highlighted in a comparative chart provided by AMD. This edge could prove pivotal in AI workloads, where memory efficiency and throughput are critical. The broader context underscores AMD’s strategic investments in TSMC’s cutting-edge nodes to fuel data center growth, with the OpenAI collaboration signaling strong early adoption. While specific future implications beyond the 2026 rollout remain limited in the coverage, the move reinforces AMD’s trajectory toward dominating AI infrastructure alongside hyperscalers.
Source: videocardz

