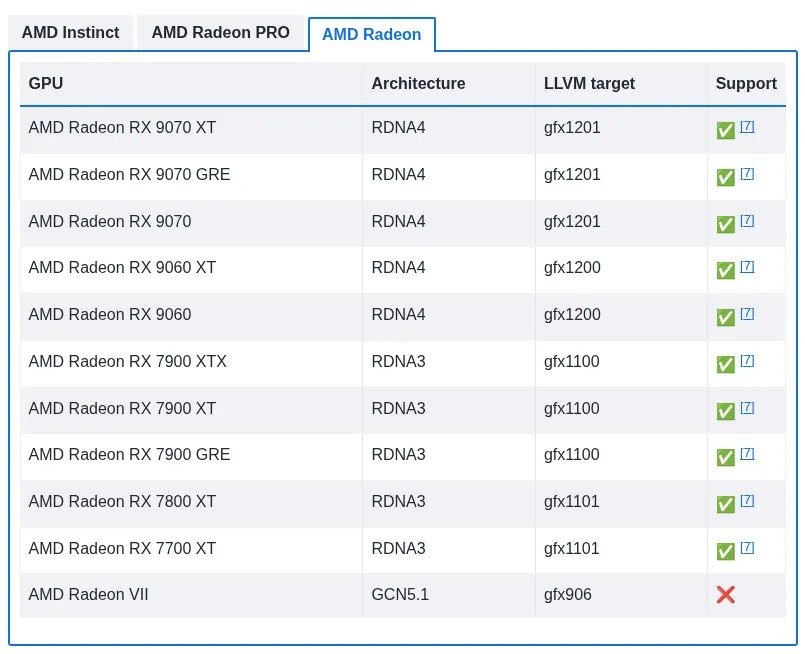
AMD has officially released ROCm 7.0.2, its open-source platform for GPU-accelerated computing, introducing long-awaited support for the Radeon RX 9060 graphics card just two months after the GPU’s initial launch. This update aligns with AMD’s prior commitment to provide full ROCm compatibility across the entire Radeon RX 9000-series lineup, a promise that wasn’t fully realized at the series’ debut. With this release, both the standard Radeon RX 9060 and the higher-end RX 9060 XT models are now officially supported, integrating seamlessly with the RX 9070 series as part of the RDNA 4 architecture family. For the first time, every current card in the RX 9000-series is fully compatible with the ROCm compute stack, enabling broader adoption for high-performance computing, machine learning, and AI workloads on consumer-grade AMD hardware.
On the technical front, the ROCm 7.0.2 update brings several enhancements to its core components. The HIP (Heterogeneous-compute Interface for Portability) runtime now includes a new flag, hipMemAllocationTypeUncached, which allows for uncached memory allocations to optimize performance in specific scenarios. Additionally, the hipBLAS library has been upgraded to better accommodate newer GPU architectures, including RDNA 3.5 variants like gfx1150 and gfx1151, as well as RDNA 4’s gfx1200 and gfx1201 targets. These improvements ensure more efficient linear algebra operations on the latest AMD silicon.
Expanding beyond hardware support, ROCm 7.0.2 adds official compatibility with several modern Linux distributions and kernels, specifically Debian 13, Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 10.0, and Oracle Linux 10, all leveraging the Linux 6.12 kernel. This broadens the platform’s accessibility for enterprise and developer environments. In terms of new features and integrations, the release incorporates Gaussian Splatting (gsplat) support directly into PyTorch for advanced 3D rendering and neural radiance field applications, alongside compatibility with PyTorch 2.8 for cutting-edge machine learning frameworks. Developers working with large language models will benefit from the inclusion of FlashInfer libraries, while native support for llama.cpp enables easier deployment of efficient inference engines on AMD GPUs.
Source: Phoronix

